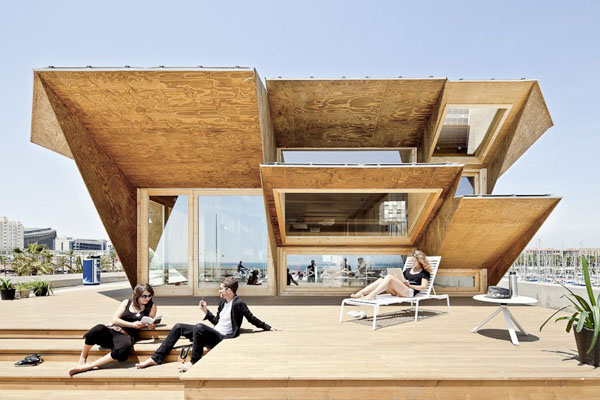
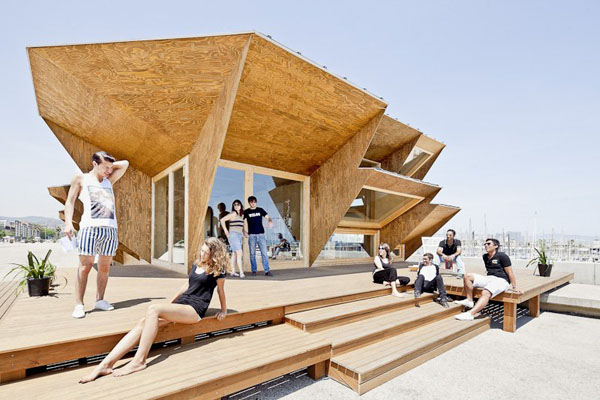
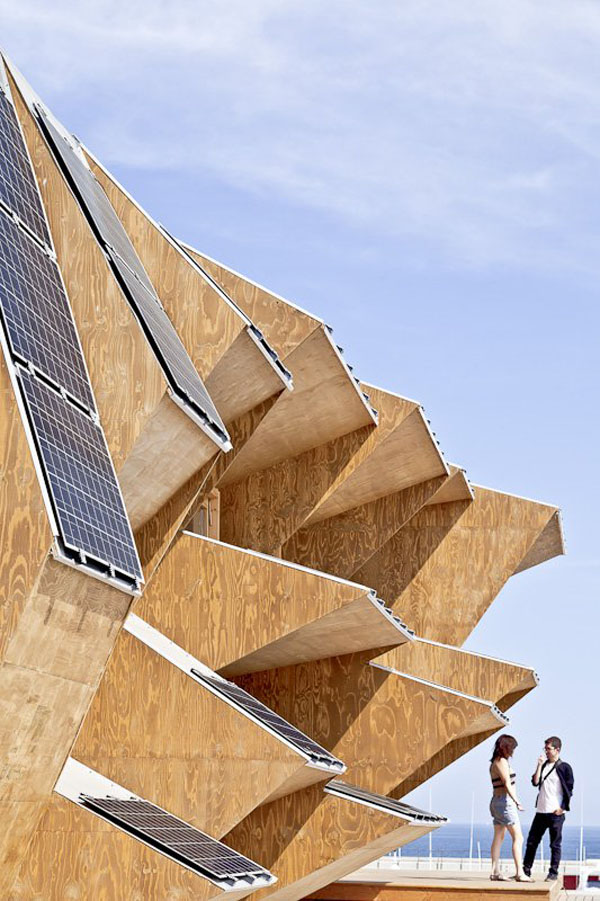
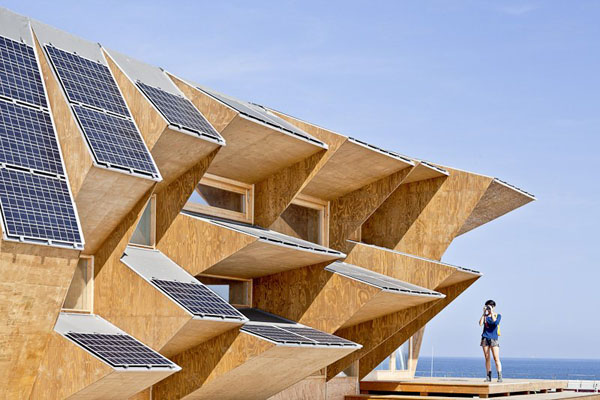
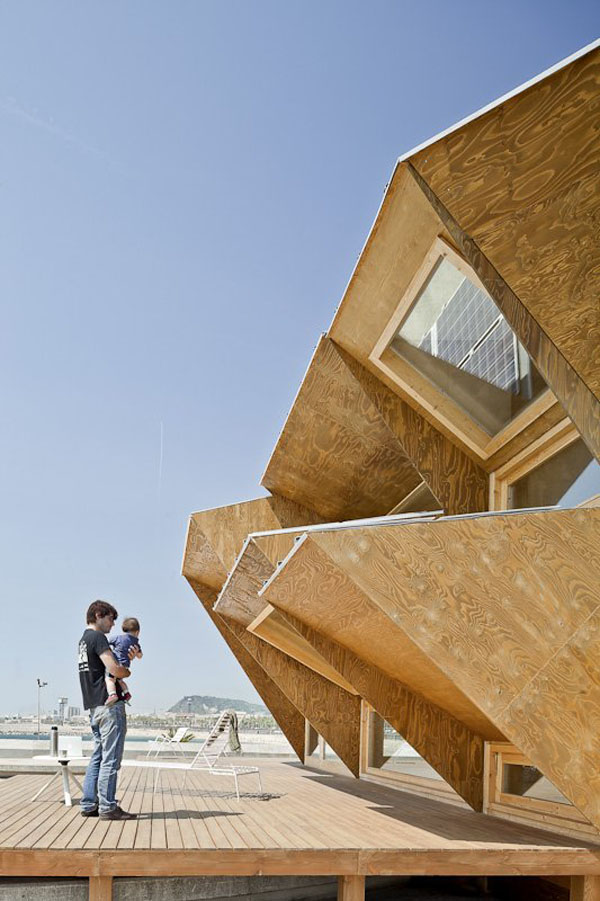
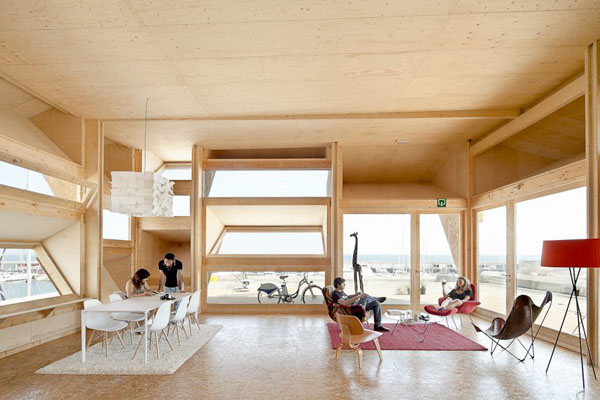
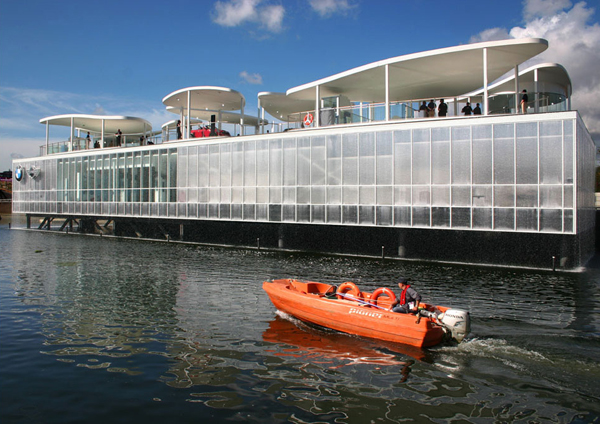
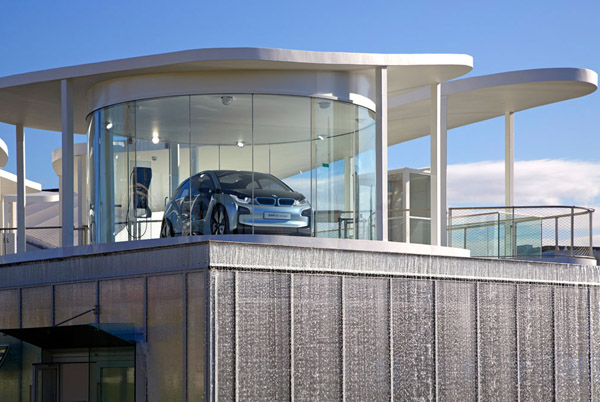
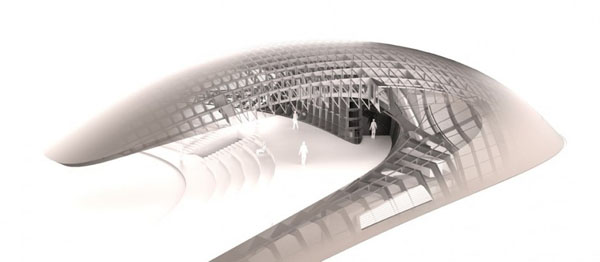
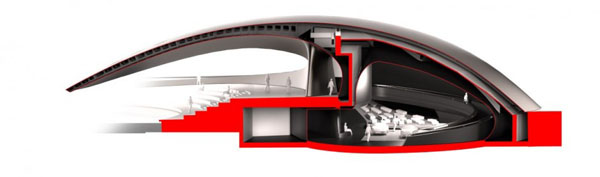
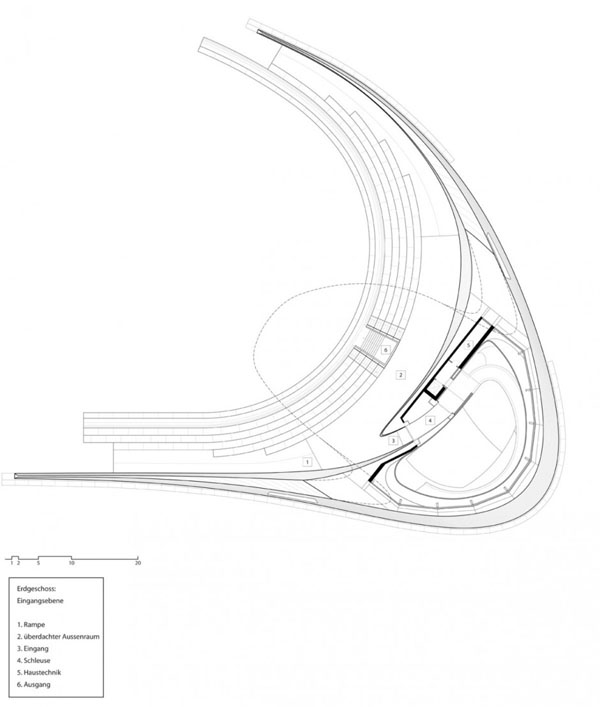
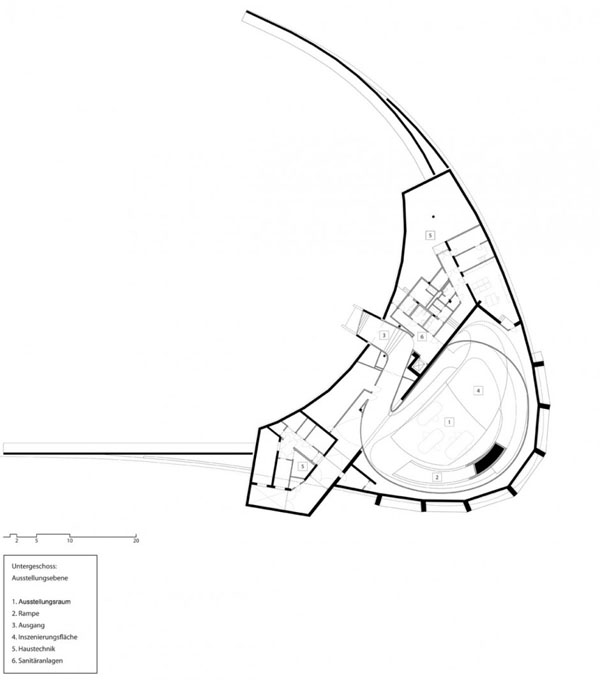
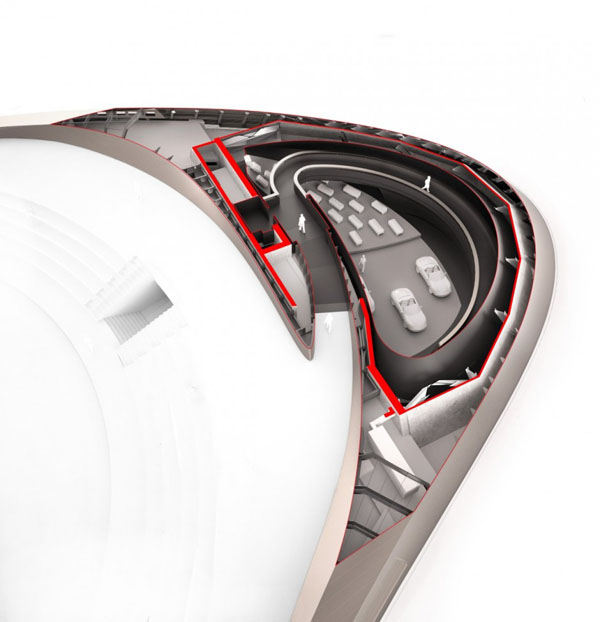
Designed by students at the Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia IAAC, the Endessa Pavilion is part of the Smart City Expo in Barcelona, Spain. The aim of the project is exploring the possiblities ofdistributed intelligence concept. The building is conceived as an adaptive system that responds to environmental influences. The skin is constructed as a network of intelligent nodes that position themselves according to solar radiation.
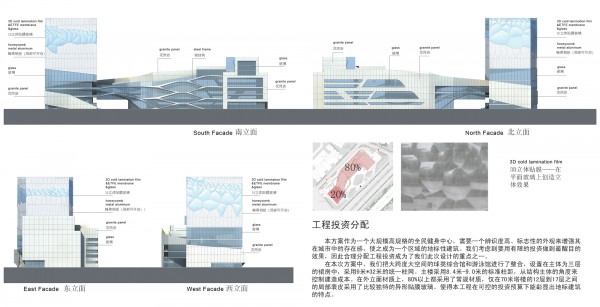
Photovoltaic panels are mounted onto the modular roof that allows radiation to enter the building during the cold months and protect the interior during summer. The design and position of these front modules not only depend on the orientation but also the relationship the building has with its environment.
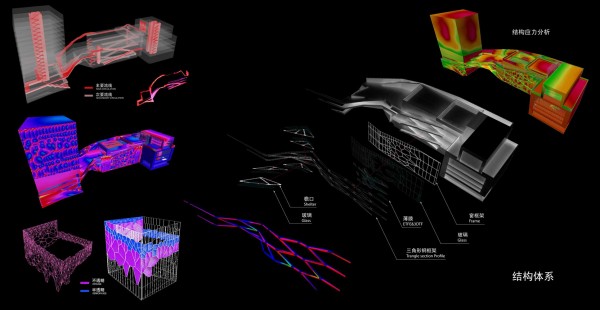
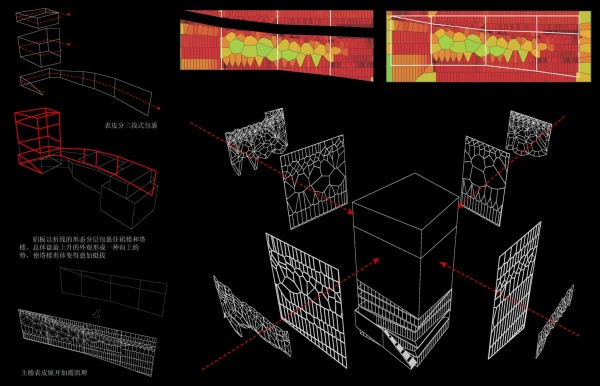
The building is designed to be fabricated by CNC machines. Built in a month, the building was assembled out of parts that were defined in digital format string and cut into very quickly, even if they were completely different from each other. Encounters between pieces have been resolved through software, and the pieces are cut into the system thinking that are in the building. With this precision, the pieces of wood come to work for meetings with the recesses and holes for receiving bolts. Perimeter facade modules are produced and assembled at the factory, so that on the work should only be fitted, further increasing the efficiency of construction.